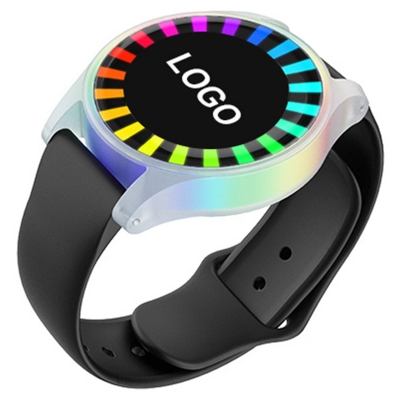
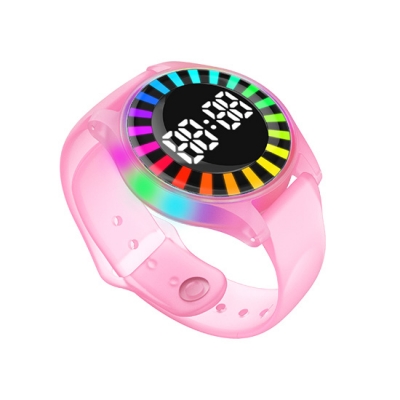
تطورت تقنية الاتصال قريب المدى (NFC) من ابتكارٍ متخصص إلى أداةٍ شاملةٍ في مختلف القطاعات. وأصبحت حجر الزاوية في التكنولوجيا الحديثة، إذ تُسهّل التواصل السلس بين الأجهزة عبر مسافاتٍ قصيرة. من المدفوعات عبر الهاتف المحمول والتحكم في الوصول إلى الملصقات الذكية وتفاعل المستهلكين، تُغيّر تقنية الاتصال قريب المدى (NFC) طريقة تفاعلنا مع العالم من حولنا.
أساسيات NFC وRFID
تقنية NFC هي فرع من تقنية تحديد الهوية بموجات الراديو (RFID)، تعمل بتردد 13.56 ميجاهرتز. بينما تُستخدم تقنية تحديد الهوية بموجات الراديو (RFID) بشكل أساسي لتحديد الهوية والتتبع لمسافات طويلة، صُممت تقنية NFC للاتصالات قصيرة المدى، عادةً ضمن نطاق 4 سم. تضمن هذه الاتصالات قريبة المدى تبادلًا آمنًا للبيانات، مما يجعلها مثالية لتطبيقات مثل الدفع عبر الهاتف المحمول والتحكم في الوصول.
يمكن لأجهزة NFC العمل في ثلاثة أوضاع:
وضع القارئ/الكاتب: يمكّن الجهاز من قراءة البيانات أو كتابتها على علامة NFC.
وضع النظير إلى النظير: يسهل تبادل البيانات بين جهازين يدعمان تقنية NFC.
وضع محاكاة البطاقة: يسمح للجهاز بالعمل كبطاقة ذكية بدون تلامس.
يفتح دمج تقنية NFC وRFID إمكانيات لا حصر لها ويؤدي إلى ظهور حلول مبتكرة تعمل على تحسين الكفاءة والأمان وتجربة المستخدم.
تطبيقات NFC الموسعة
الدفع عبر الهاتف المحمول
أحدثت تقنية NFC ثورةً في قطاع الدفع الإلكتروني بتمكينها المعاملات اللاتلامسية. فبلمسة زر واحدة، يمكن للمستخدمين الدفع باستخدام هواتفهم الذكية أو ساعاتهم الذكية أو بطاقاتهم المزوّدة بها. وتُستخدم هذه التقنية على نطاق واسع لسهولتها وسرعتها وأمانها. على سبيل المثال، تعتمد خدمات مثل Apple Pay وGoogle Wallet وSamsung Pay على تقنية NFC لإجراء معاملات سلسة.
التحكم في الوصول
تُستخدم تقنية NFC على نطاق واسع في أنظمة التحكم في الدخول، لتحل محل المفاتيح والبطاقات التقليدية. توفر أساور المعصم وسلاسل المفاتيح والبطاقات المزودة بتقنية NFC وصولاً آمنًا ومريحًا إلى المباني والمركبات والمناطق المحظورة. على سبيل المثال، " سوار NFC للتحكم في الوصول سوار معصم سيليكوني بتقنية تحديد الهوية بموجات الراديو (RFID) قابل لإعادة الاستخدام، مصمم للتحكم في الدخول. مصنوع من سيليكون عالي الجودة، يضمن ملاءمة آمنة ومريحة، مما يجعله مثاليًا للاستخدام طويل الأمد في الفعاليات والصالات الرياضية وأماكن العمل.
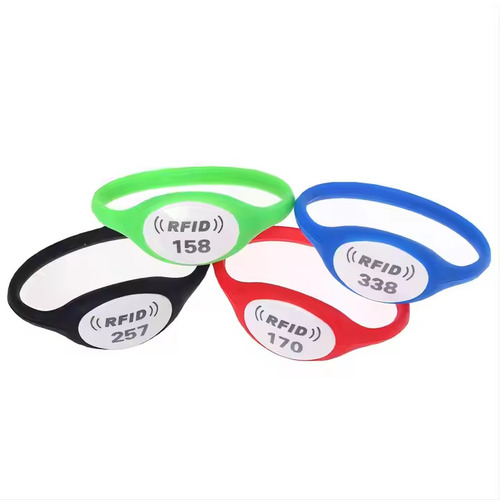


ملصقات ذكية
تتيح الملصقات الذكية المزودة بعلامات NFC للمستخدمين الحصول على مزيد من المعلومات بمجرد لمس هواتفهم الذكية. تُستخدم هذه التقنية على نطاق واسع في مجالات التسويق والسياحة والتعليم. على سبيل المثال، يمكن للمتاحف استخدام الملصقات الذكية لتزويد الزوار بمعلومات مفصلة عن المعروضات، بينما يمكن لتجار التجزئة استخدامها للترويج للمنتجات والعروض.
مشاركة المستهلك
تُعزز تقنية NFC تفاعل المستهلكين من خلال توفير تجارب تفاعلية. يمكن للشركات استخدام البطاقات أو سلاسل المفاتيح المزوّدة بتقنية NFC لتخزين روابط مواقع التواصل الاجتماعي، أو المحتوى الترويجي، أو تفاصيل برامج العضوية. بطاقة NFC قابلة للطباعة لوسائل التواصل الاجتماعي "مثال جيد. يتميز بشريحة ذكية مدمجة قابلة لإعادة البرمجة، وطباعة مخصصة عالية الجودة، مما يجعله أداة فعّالة للعلامات التجارية والتواصل.


التآزر بين تقنية NFC وتقنية RFID
يُسهم دمج تقنيتي NFC وRFID في بناء منظومة قوية تُحسّن الكفاءة والأمان. تُعدّ تقنية RFID مثاليةً للتحديد والتتبع بعيد المدى، بينما تُعدّ تقنية NFC مثاليةً لتبادل البيانات الآمن قصير المدى. ويُتيح كلاهما، معًا، مجموعةً واسعةً من التطبيقات، من إدارة سلسلة التوريد إلى المدن الذكية.
على سبيل المثال، في قطاع التجزئة، يُمكن استخدام تقنية تحديد الهوية بموجات الراديو (RFID) لإدارة المخزون، بينما تُسهّل تقنية الاتصال قريب المدى (NFC) الدفع بدون تلامس والتفاعل مع العملاء. وفي قطاع الرعاية الصحية، يُمكن لتقنية تحديد الهوية بموجات الراديو تتبع الأجهزة الطبية، بينما تضمن تقنية الاتصال قريب المدى (NFC) الوصول الآمن إلى السجلات الطبية.
التحديات والتوقعات المستقبلية
على الرغم من المزايا العديدة لتقنية NFC، إلا أنها تواجه تحديات عديدة، منها المخاوف الأمنية، ومشاكل التوافق، ومحدودية استخدامها في بعض المناطق. ومع ذلك، فإن التقدم المستمر في تقنيات التشفير، والتوحيد القياسي، وتوعية المستخدمين يُسهم في معالجة هذه التحديات.
مستقبل تقنية NFC واعد، مع ظهور العديد من التطبيقات الناشئة في مجالات مثل إنترنت الأشياء (IoT)، والتكنولوجيا القابلة للارتداء، والمنازل الذكية. على سبيل المثال، يمكن للأجهزة القابلة للارتداء المزودة بتقنية NFC مراقبة المؤشرات الصحية، بينما يمكن لأجهزة المنزل الذكي استخدام تقنية NFC للتحكم والأتمتة بسلاسة.
خاتمة
حققت تقنية NFC تقدمًا كبيرًا منذ نشأتها، حيث غيّرت مشهد الصناعة وحسّنت تجربة المستخدم. وقد أثبتت تطبيقات NFC في مجالات مثل الدفع عبر الهاتف المحمول، والتحكم في الوصول، والملصقات الذكية، وتفاعل المستهلك تنوعها وإمكانياتها. ومن خلال الاستفادة من التكامل بين NFC وRFID، يمكن للشركات والأفراد فتح آفاق جديدة للكفاءة والأمان والابتكار. ومع استمرار تطور التكنولوجيا، ستلعب تقنية NFC بلا شك دورًا محوريًا في بناء عالم أكثر ذكاءً وترابطًا.